JavaWeb
Spring
学习来源于B站狂神说
介绍
Spring框架是一个开放源代码的J2EE应用程序框架,由[Rod Johnson](https://baike.baidu.com/item/Rod Johnson/1423612)发起,是针对bean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器(lightweight container)。 Spring解决了开发者在J2EE开发中遇到的许多常见的问题,提供了功能强大IOC、AOP及Web MVC等功能。Spring可以单独应用于构筑应用程序,也可以和Struts、Webwork、Tapestry等众多Web框架组合使用,并且可以与 Swing等桌面应用程序AP组合。因此, Spring不仅仅能应用于J2EE应用程序之中,也可以应用于桌面应用程序以及小应用程序之中。Spring框架主要由七部分组成,分别是 Spring Core、 Spring AOP、 Spring ORM、 Spring DAO、Spring Context、 Spring Web和 Spring Web MVC。 -百度百科
相关文档:
- Spring Framework
- Spring Framework Overview
- Overview (Spring Framework 5.3.22 API)
- GitHub - spring-projects/spring-framework: Spring Framework
- Maven Repository: org.springframework » spring-webmvc (mvnrepository.com)
SSM:
- Spring
- Spring MVC
- Mybatis
优点
- 开源免费的容器(框架)
- 轻量级、非入侵式框架
- 控制反转(IOC)、面向切面编程(AOP)
- 支持事务处理,对框架整合的支持
- 总结:Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)和面向切面(AOP)编程的框架
扩展
Spring Boot
- 一个快速开发的脚手架
- 基于SpringBoot可以快速开发单个微服务
- 约定大于配置
Spring Cloud
- SpringCloud基于SpringBoot实现
IOC
简单入门:-> Spring01
UserDao接口
UserDaoImpl实现类
UserService业务接口
UserServiceImpl业务实现
-> Spring02
Hello 对象是谁创建的?
- hello对象是由Spring创建的
Hello对象的属性是怎么设置的?
- hello对象的属性是由Spring容器设置的,这个过程就叫控制反转:
- 控制:谁来控制对象的创建,传统应用程序的对象是由程序本身控制创建的,使用Spring后,对象是由Spring来创建的.
- 反转:程序本身不创建对象,而变成被动的接收对象.
- 依赖注入:就是利用set方法来进行注入的.
IOC是一种编程思想,由主动的编程变成被动的接收,可以通过newClassPathXmlApplicationContext去浏览一下底层源码 。OK ,到了现在,我们彻底不用再程序中去改动了,要实现不同的操作,只需要在xm|配置文件中进行
构造函数
-> Spring03
在配置文件加载的时候,容器中管理的对象就已经初始化了
spring默认使用无参构造函数创建bean
index索引
1
2
3
4<bean id="user" class="org.example.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="hello"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>属性名
1
2
3
4<bean id="user" class="org.example.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="hello"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>属性类型(不推荐,同个类型的多个变量你咋整)
1
2
3
4<bean id="user" class="org.example.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="hello"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="int" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>Spring配置
-> Spring03
别名-alias
1 | <!--todo alias 别名: name对应id所属bean, alias可以起别名--> |
bean配置
1 | <!--todo bean配置 |
import
一般用于团队开发使用:可以将多个配置文件,导入合并为一个
1 | <import resource="beans.xml"/> |
DI依赖注入
-> Spring04
构造器注入
同构造函数(spring03)
Set方式注入
1 | <!--todo set注入--> |
拓展方式注入
1 | <!--todo p命名空间注入 直接注入属性的值 property--> |
Bean作用域(scopes)
1 | <!--todo 单例模式 - 默认机制 - 保持所有创建的对象都为单例--> |
测试
1 | /** |
自动装配beans(重点)
- 自动装配是Spring满足bean依赖一种方式
- Spring会在 上下文中自动寻找,并自动给bean装配属性!
在Spring中有三种装配的方式
在xml中显式的配置
-> Spring05
首先导入需要装配的bean
1
2<bean id="dog" class="org.example.dao.Dog"></bean>
<bean id="cat" class="org.example.dao.Cat"></bean>byname的时候,需要保证所有bean的id唯一, 并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的set方法的值一致!
1
2
3
4<!--todo 按名称byname 需要保证所有bean的id唯一, 并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的set方法的值一致-->
<bean id="human" class="org.example.dao.Human" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="小明"/>
</bean>bytype的时候,需要保证所有bean的class唯一, 并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的类型一致!
1
2
3
4<!--todo 按类型bytype 需要保证所有bean的class唯一-->
<bean id="human" class="org.example.dao.Human" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="小明"/>
</bean>
在java中显示配置 - 注解实现自动装配
-> Spring07
指定要扫描的包
1
2<!--todo 指定要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="org.example.pojo"/>开启注解支持
1
2<!--todo 开启注解支持-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>注解实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/*todo Component组件:等价于<bean id="human" class="org.example.pojo.Human"/>*/
/*@Scope("prototype") 作用域设置*/
public class Human {
/*todo Value : 相当于<property name="name" value="小明"/>*/
private String name;
private Dog dog;
private Cat cat;
//......
}@Component有几个衍生注解,我们在web开发中,会按照mvc三层架构分层!
dao [@Repository]
service [@Service]
controller [ @Controller]
这四个注解功能都是一样的,都是代表将某个类注册到Spring中,装配Bean
隐式的自动装配bean [重要]
-> Spring06
开启注解支持
1
2<!--todo 开启注解支持-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>导入bean
1
2
3
4<bean id="human" class="org.example.dao.Human"></bean>
<bean id="cat1" class="org.example.dao.Cat"/>
<bean id="cat2" class="org.example.dao.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog1" class="org.example.dao.Dog"/>
@Resource和@ Autowired的区别:都是用来自动装配的,都可以放在属性字段上
@Autowired通过byname的方式实现,而且必须要求这个对象存在!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12/* todo 使用注解就可以不用编写set方法了
* 可以在属性上使用也可以在set方法上使用
* Autowired:先找类型再找名称
* Qualifier可以指定bean唯一的注入对象
* 如果@Autowired自动装配的环境比较复杂,自动装配无法通过一个注解[@Autowired] 完成的时候、我们可以
* 使用@Qualifier(value=" xxx' )去配置@Autowired的使用,指定一个唯-的bean对象注入!
* */
//todo Nullable说明该字段可以为空
//@Nullable
private Cat cat;@Resource默认通过byname的方式实现,如果找不到名字,则通过byType实现!如果两个都找不到的情况下,就报错
1
2
3/*todo Resource:先名字后类型*/
private Dog dog;xml与注解:
- xml更加万能,适用于任何场合!维护简单方便
- 注解不是自己类使用不了,维护相对复杂!
- xml与注解最佳实践:
- xml用来管理bean;
- 注解只负责完成属性的注入;
- 我们在使用的过程中,只需要注意一个问题:必须让注解生效,就需要开启注解的支持
使用Java方式装配Spring
-> Spring08
直接使用java类的方式去实现配置
1 | package org.example.config; |
使用方法有所改变:如下:
1 |
|
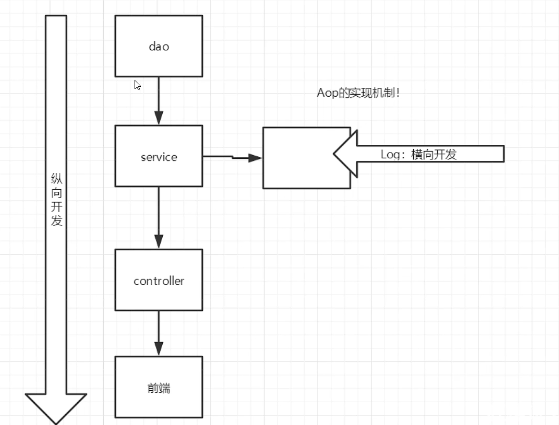
AOP
使用Spring实现AOP
-> Spring09
横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。即是,与我们业务逻辑无关的,但是我们需要关注的部分,就是横切关注点。如日志,安全,缓存,事务等等…
- 切面(ASPECT) :横切关注点被模块化的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
- 通知(Advice) :切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一一个方法。
- 目标(Target) :被通知对象。
- 代理(Proxy) :向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
- 切入点(PointCut) :切面通知执行的“地点”的定义。
- 连接点JointPoint) :与切入点匹配的执行点。
方式一:使用spring API接口实现aop
1 | <!--todo 方式一:spring api接口配置--> |
方式二:自定义实现aop(主要是切面定义)
首先定义方法执行前后要执行的函数
1 | package org.example.diy; |
其次,在xml文件中进行AOP切入
1 | <!--todo 方式二:使用自定义实现AOP(主要是切面定义)--> |
方式三:使用注解方式
首先,创建注解类去实现AOP,注意一下切入的执行顺序
1 | package org.example.diy; |
其次在beans.xml文件中去导入bean和开启注解支持
1 | <!--todo 方式三:使用注解方式--> |
结合Mybatis
步骤:
导入相关jar包
- junit
- mybatis
- mysq|数据库
- spring相关的
- aop注入
- mybatis-spring [new]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.29</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.22</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.22</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.9.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>编写配置文件
测试
整合Spring
编写数据源配置
将大部分mybatis操作写至spring-dao.xml文件中去
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--todo 使用Spring提供的JDBC-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="333333"/>
</bean>
</beans>mybatis-config只需简单配置包别名即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
<configuration>
<!--todo 包别名-->
<!-- 引用的包的类默认小写-驼峰命名-->
<typeAliases>
<package name="org.example.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
</configuration>sqlSessionFactory
在spring-dao.xml配置sqlSessionFactory并引入mybatis-config配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7<!--sqlSessionFactory-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!--绑定Mybatis配置文件-->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:org/example/dao/*.xml"/>
</bean>sqISessionTemplate
在spring-dao.xml配置sqISessionTemplate
1
2
3
4<!--SqlSessionTemplate 就是之前的sqlSession-->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>需要给接口加实现类【】
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20package org.example.dao;
import org.example.pojo.Dept;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import java.util.List;
public class DeptMapperImpl implements DeptMapper1 {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void setSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
}
public List<Dept> getAllDept() {
DeptMapper1 mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DeptMapper1.class);
return mapper.getAllDept();
}
}将自己写的实现类,注入到Spring中,
1
2
3<bean id="deptMapper" class="org.example.dao.DeptMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession"></property>
</bean>测试使用即可!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void test() throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DeptMapper1 deptMapper = context.getBean("deptMapper", DeptMapper1.class);
for (Dept dept : deptMapper.getAllDept()) {
System.out.println(dept);
}
}另有方式二,看代码->DeptMapperImpl2
声明式事务
-> Spring11
事务
- 把一组业务当成- -个业务来做;要么都成功,要么都失败!
- 事务在项目开发中,十分的重要,涉及到数据的一致性问题,不能马虎!
- 确保完整性和一致性
事务的作用:如果不配置事务,可能存在数据提交不一致的情况
事务ACID原则:
原子性
一致性
隔离性
多个业务可能操作同-个资源,防止数据损坏
持久性
事务一旦提交,无论系统发生什么问题,结果都不会再被影响,被持久化的写到存储器中!
spring中的事务管理
声明式事务:AOP
全程在spring-dao.xml文件进行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24<!--todo 1. 配置声明式事务-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--todo 结合AOP实现事务植入-->
<!--todo 2. 配置事务通知-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--todo 3.给予那些方法配置事务-->
<!--todo 4.配置事务的传播特性:new propagation-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="add" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="query" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--todo 5.配置事务切入-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointCut" expression="execution(* org.example.mapper.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut"/>
</aop:config>编程式事务:代码中进行事务管理